Overview
Present import indicates how Classification Classes may be imported in the system.
The purpose and the scope of this document is to describe the file format specifications for the import of Classification Classes.
Overall Conventions
Software
Import filters file is composed of one XLSX sheet. Therefore, to build the file a program needs to be installed that can handle the XLSX format, such as Microsoft Excel. Documents which implement this file format specification need to be saved as .xlsx files.
Worksheet
An Excel file can be structured in multiple work sheets. Each work sheet has a name that must be adhered to.
Each sheet has two header lines and a data payload.
In row 1 the human readable column names are printed – the row will be ignored by import
Row 2 contains the column codes that are used by the import program to identify the content.
Then follow the data rows.
Table Columns
Column name
Each table column has a name which gives a human comprehensive short reference of the column's content.
Note: the column name is for convenience only and not used to interpret the file.
Column Code
In order to reference the column unambiguously each column gets a unique code within the worksheet.
The import program is relying on Column Codes. If Column orders are changed, the codes must be preserved.
Requirement of Contained Data
Each column of contained data can be either
-
Mandatory – values MUST be present
-
Optional – values MAY be present
-
Conditional – values MUST be present IF a condition applies
Data types
Each column has a defined data type, i.e. a restricted set of available values. For example the data type integer only allows whole numbers while the data type string allows any sequences of characters. Additionally the data type string can be syntactically further constrained by a grammar.
|
Data type |
Description |
Example |
|
Integer |
whole number (positive and negative) |
-10, 20 |
|
Real |
Rational numbers (positive and negative)
|
10, 10.5, -12,44
|
|
String |
Sequence of characters (excluding inverted comma)
|
AbC |
Column Description
Description of the content for each column.
Translatability
The content of each column can be either translatable of not. In case a column's content data are translatable, the column code in the header is suffixed by a locale code comprising of a language code, an underscore and a country code. Example of locale codes: "de_DE", "en_US".
IN/OUT
For each column it can be defined whether the contained data is relevant for import or only gives additional information to a human reader of the file.
Identifiers (IDs)
References within the exchange file are made by an ID. There are two kinds of IDs to be separated:
-
Transient ID
Any sequence of characters can be treated as a transient ID when it cannot be confused with a code or an IRDI. It is recommended to use 6 digits long zero padded running numbers, e.g. 000001. The running number must be unique within the file and will be replaced by a code during import.
-
Persistent ID
A persistent ID can be used for references during load of new entries and for updates of existing entries. For updates of data that are already stored in eptos using a persistent ID is mandatory. The format of the persistent ID in eptos is the international registration data identifier (IRDI). For classification classes also the coded name may be used.
When an import file contains more than one ID for the same entity, the following precedence is taken:
-
Persistent ID (IRDI)
-
Coded Name
-
Transient ID
Definitions, Acronyms and Abbreviations
IRDI – Format of identifier according to ISO29002-5
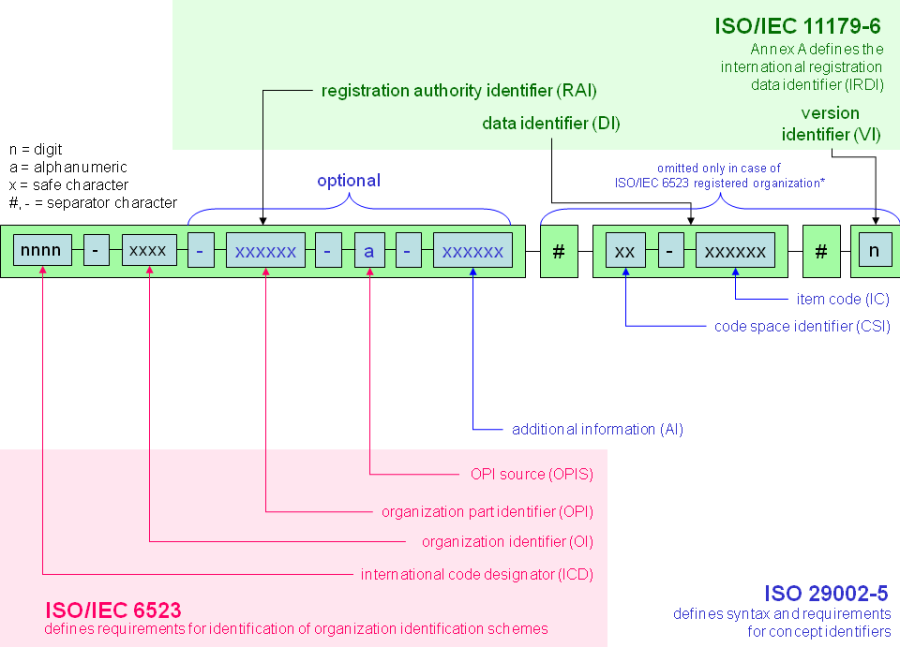
Abbildung1 – IRDI syntax
[This subsection should provide the definitions of all terms, acronyms, and abbreviations required to interpret properly the Modern SRS. This information may be provided by reference to the project Glossary.]
References
[This subsection should provide a complete list of all documents referenced elsewhere in the Modern SRS. Each document should be identified by title, report number (if applicable), date, and publishing organization. Specify the sources from which the references can be obtained. This information may be provided by reference to an appendix or to another document.]
Overview
[This subsection should describe what the rest of the Modern SRS contains and explain how te Modern SRS is organized.]
Import of Classification Classes
|
Column name |
Obligation |
IN/OUT |
Column Code |
Value Data Type |
Description |
Translatable |
|
Superclass |
M/O |
IN/OUT |
C01 |
String |
IRDI/SCV of the Parent Class or an internal ID (see column C02) denoting the Parent Class (when part of same file).
|
N |
|
ID |
M |
IN/OUT |
C02 |
String |
For NEW CLASS: it contains either an internal ID identifying the class OR user-proposed IRDI/SCV.
|
N |
|
Hierarchical position |
M |
IN/OUT |
C03 |
String |
Hierarchical position of classification class
|
N |
|
Preferred Name |
M |
IN/OUT |
C04 (langCode) |
String |
Preferred Name of the Classification Class to be imported. Lang code is in the form e.g. EN, DE. Column is not mandatory when updating a class (see note 4)Preferred name should be validated against business rules (see note 7) |
Y |
|
Definition |
O |
IN/OUT |
C05 (langCode) |
String |
Definition of the Classification Class |
Y |
|
Source |
O |
IN/OUT |
C06 (langCode) |
String |
Source of definition of the Classification Class |
Y |
|
Remark |
O |
IN/OUT |
C07 (langCode) |
String |
Remark regarding Classification Class to be imported |
Y |
|
Creation date |
O |
IN/OUT |
C09 |
String |
Date when the version is created. Format is yyyy-mm-dd according ISO 8601 (example: "2011-01-15") and the Excel cell should be String. |
N |
|
Revision number |
O |
IN/OUT |
C10 |
Integer |
The revision number is a number that serves for administration of revision. |
N |
|
Primary language |
M |
IN/OUT |
C11 |
String with syntax "langCode_countryCode" |
Localized language in which the Classification Class was initially defined (e.g. "en_US"). Column is not mandatory when updating a class (see note 4) |
N |
|
Restricted |
O |
IN/OUT |
C12 |
String |
May contain values "Y" or "N". |
N |
|
Hierarchical position of superclass |
O |
IN/OUT |
C13 |
String |
Hierarchical position of superclass
|
N |
|
IRDI for a posteriori case of |
O |
IN/OUT |
C14 |
String |
Identification (IRDI/SCV) of classification class for a posteriori case of.
|
N |
|
Hierarchical position for a posteriori case of |
O |
IN/OUT |
C15 |
String |
Identification (hierarchical position) of classification class from external dictionary. |
N |
|
Preferred name (Short) |
M/O |
IN/OUT |
C16 |
String |
Short Preferred Name of the Classification Class to be imported. Lang code is in the form e.g. EN, DE. Column is not mandatory when updating a class (see note 4)
|
Y |
|
Preferred name (Materialgroups) |
O |
IN/OUT |
C17 |
String |
Preferred name regarding material groups |
Y |
|
Deprecated |
O |
IN/OUT |
C18 |
String |
empty Class is deprecated yes/no |
N |
|
Predecessor List |
O |
OUT |
C19 |
String |
comma separated list of predecessor classes |
N |
|
Importable raw column |
O |
IN/OUT |
RAW (CODE) |
String |
Any flag or value that can be set to a field previously marked as "importable". See note10.
|
N |
|
Code from name |
O |
OUT |
C20 |
String |
Coded name extracted if the CC name is something specific like "12345678 My Name", otherwise empty |
N |
|
Version |
O |
OUT |
C21 |
String |
Version |
N |
|
Code mapped class |
O |
OUT |
C22 |
String |
Code mapped class |
N |
|
Coded name mapped class |
O |
OUT |
C23 |
String |
Coded name mapped class |
N |
|
Business responsible |
O |
OUT |
C24 |
String |
Business responsible of respective class |
N |
|
Deprecation date |
O |
OUT |
C25 |
String |
Date when class has been deactivated, if it is the case. |
N |
Note1: If empty, optional columns will be ignored for Import.
Note2: For translatable attributes column will be multiplied in import file for each needed language.
Note3: in case the option "Natural key"/"spechender Schlüssel" is being selected then the column superclass will be ignored and the hierarchy will be calculated :
-
For syntax-aware hierarchies, based on the syntax for children/parent codednames
-
For no-syntax hierarchies, based on column "hierarchical position" / "hierarchical position of superclass" (which becomes mandatory)
Note4: update of existing elements is possible by selecting option "Allow update" and specifying as ID an existing element. Only the textual fields (e.g. preferred name, preferred name (short), definition, source, remark) will be updated with the new content.
Note5: If column "Restricted" is empty, system will import respective Classifications as non-restricted.
Note6:Imported classification class will be connected with this class by a posteriori case of relation.
Used to denote that imported class was adapted from this class. If both IRDI/SCV (C14) and Hierarchical position (C15) are present IRDI/SCV has precedence, value of C15 is ignored.
Since hierarchical position can't specify a class from external dictionary and we want to cover this also, import GUI will allow selection of release from which classes specified by column C15 belongs.
Note7:For some classification class types (e.g. FOUR_LEVEL_EIGHT_DIGIT_NO_SYNTAX) specific checks and corrections may apply. Check definition of each classification class type.
Note 8: The successor classes are maintained in the system according to the use case, therefore C19 only exports the derived predecessor list. No import.
Note9: For PFC enabled dictionaries, column C16 Preferred name(short) is mandatory
Note10: An importable RAW column allows a value to be imported for a class in a field that does not have or need additional implementation. One only needs to know the unique identifier from Eptos of that modeled field.
